Volume 22, No.4
November issue 2017
1. 最近の研究から/FROM LATEST RESEARCH
Department of Chemistry, National Taiwan University
- Abstract
- Oxygen evolution reaction (OER) is a half reaction of water splitting. Toward this end, transition-metal oxides have been demonstrated to act as electrocatalysts for OER. Among various transition-metal oxides, 3d transition metals with spinel structures were widely used for being active electrocatalysts toward this reaction. Nevertheless, spinel is a complex structure, in which two oxidation state of metal ions as well as two different crystallographic sites are present in this structure. To investigate the behavior of spinel structure during OER, we have developed both in-situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy and in-situ grazing-angle X-ray diffraction manner, while various well-designed samples were prepared to figure out the dominated factors step by step. First, we have modified the electrocatalysts with surface reversibly adapting layer to improve the resulting stability. Second, we choose the spinel structure with bimetallic system of NiCo2O4 to reveal the active cite between these two metals. Furthermore, the non-active metals were employed to substitute for the divalent and trivalent metal ions in spinel to point out the active centers. The effects of crystallographic sites were verified by a model system of inverse spinel Fe3O4 with replacing by Co, Ni, and Zn divalent metal ions. As a result, we can clarify that the divalent metal ions are the active center for OER in the spinel structure, while a phase transformation to metal oxyhydroxide which act as the real active phase is needed to achieve a higher performance. From the result of understanding spinel behavior toward OER, we can realize that the in-situ X-ray spectroscopy is a useful technique, and believed that this technique can be used not only in spinel structure but other catalyst for other reactions.
(国)量子科学技術研究開発機構 放射光科学研究センター Synchrotron Radiation Research Center, National Institutes for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology
- Abstract
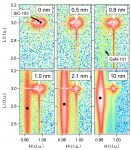
- 窒化ガリウム(GaN)薄膜の成長初期にのみ発現する特異な格子変形現象を報告する。SPring-8、量研(QST)専用ビームラインBL11XUでは、結晶成長装置とX線回折計が一体化した独自のその場測定装置を有している。本研究は、GaN薄膜成長中のその場X線回折を原子層オーダーの膜厚分解能で測定し、GaNの面内および面内垂直方向の格子間隔の変化を詳細に調べた。その結果、膜厚数ナノメートルの成長初期にのみ、従来の弾性変形とは異なる特異な格子変形を見出した。この現象を理解するため、従来の弾性ひずみに加えて、点欠陥の混入による単位格子の膨張効果を取り入れた格子変形モデルを構築し、実験結果を良く再現することができた。このことから、GaN薄膜は基板との格子不整合によって生じる弾性ひずみがきっかけとなり、置換型の点欠陥(アンチサイト欠陥)が形成されやすいことを示唆した。これまで見過ごされていた成長初期の点欠陥の混入は、GaNベースの発光および電子デバイスの構造設計において重要な知見を与えるものと考える。
[1](国)量子科学技術研究開発機構 量子ビーム科学研究部門 Quantum Beam Science Research Directorate, National Institutes for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology、[2]東北大学 金属材料研究所 Institute for Materials Research, Tohoku University、[3]東北大学 材料科学高等研究所 WPI-Advanced Institute for Materials Research, Tohoku University
- Abstract
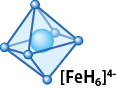
- 機能性材料実現をめざして新規水素化物の探索研究を進めている。第一原理計算による理論予測をもとに、放射光その場観察技術を援用し、新規水素化物合成を行った結果を紹介する。高エネルギー密度の水素貯蔵を目的に、資源量豊富な鉄をベースとする水素化物合成を試みた。これまで報告例のなかった3d遷移金属の水素錯体とリチウムの組み合わせからなるLi4FeH6、および、H−イオンと水素錯体が共存するLi3AlFeH8の合成に成功した。また後者の合成条件探索の過程で別の新規水素化物LiAlFeH6の合成にも成功した。
東北大学大学院 理学研究科 Graduate School of Science, Tohoku University
- Abstract
- 本研究(長期利用課題2013B0104-2016A0104)では、BL10XUに導入したメスバウア分光システムと放射光粉末X線回折実験を用いて、高温高圧下において地球核を構成する鉄・軽元素合金の相関係と磁性を明らかにした。また、下部マントルと核マントル境界におけるマグマと揮発性物質を含む鉱物の相関係と物性を明らかにした。hcp構造のFe-Si合金において電子トポロジカル転移を示唆するアイソマシフトの不連続的な増加を見出した。この転移は、金星などの地球外の惑星核にも見出される可能性がある。下部マントルと核マントル境界における相関係と物性については、マグマを模擬した玄武岩質ガラスにおいて、下部マントル条件ではFe2+、Fe3+が高スピン状態であることを明らかにした。水素および炭素の地球深部での挙動を明らかにし、下部マントルと核マントル境界でのダイヤモンドの生成、水素の存在様式を明らかにした。
名古屋大学大学院 工学研究科 Graduate School of Engineering, Nagoya University
- Abstract
- 大規模集積回路の基本素子である金属−絶縁膜−半導体電界効果トランジスタの低消費電力化・高性能化の要となるIV族系半導体材料を中心に、次世代の材料プロセス技術の開発に指針を与える各種物性発現メカニズムの解明や評価技術の構築を目的とし、BL47XUに設置されている硬X線光電子分光(HAXPES: Hard X-ray Photoemission Spectroscopy)を活用し、薄膜多層構造や微細構造における化学結合および電子状態の精密評価を推進した。各材料の物性を最大限に引き出すためには、電気的特性と密接に関連する絶縁膜/半導体の界面物性などの理解は必須であり、実デバイス内の様々な材料で構成されるナノメートルスケールの多層構造や埋もれた界面を高感度に非破壊で分析可能なHAXPESは極めて強力な分析技術である。本稿では、長期利用課題を通して得られた成果の一部を紹介する。
2. 研究会等報告/WORKSHOP AND COMMITTEE REPORT
(国)理化学研究所 先端光源開発研究部門 Innovative Light Sources Division, RIKEN SPring-8 Center
(公財)高輝度光科学研究センター 利用研究促進部門 Research & Utilization Division, JASRI
[1]大阪大学 蛋白質研究所 Institute for Protein Research, Osaka University、[2](公財)高輝度光科学研究センター タンパク質結晶解析推進室 Protein Crystal Analysis Division, JASRI
(公財)高輝度光科学研究センター 産業利用推進室 Industrial Application Division, JASRI
[1]SPring-8ユーザー協同体(SPRUC)行事幹事/広島大学大学院 理学研究科 Graduate School of Sciences, Hiroshima University、[2]九州大学大学院 総合理工学研究院 Faculty of Engineering Sciences, Kyusyu University
(公財)高輝度光科学研究センター 利用研究促進部門 Research & Utilization Division, JASRI
SPring-8ユーザー協同体(SPRUC)企画委員長/筑波大学 数理物質系 SPring-8 Users Community, Project Supervisor / Faculty of Pure and Applied Sciences, University of Tsukuba
3. SPring-8/SACLA通信/SPring-8/SACLA COMMUNICATIONS
4. 談話室・ユーザー便り/USER LOUNGE・LETTERS FROM USERS
(公財)高輝度光科学研究センター タンパク質結晶解析推進室 Protein Crystal Analysis Division, JASRI