Volume 19, No.1
February issue 2014
1. 最近の研究から/FROM LATEST RESEARCH
[1]Department of Chemistry, University of Michigan, [2]Physics Department, University of Houston, [3]Research & Utilization Division, JASRI, [4]Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, University of Tennessee
- Abstract
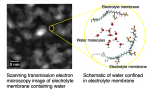
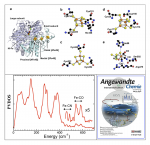
- Water under nano-confinement is known to exhibit different properties from that of bulk water. Recent neutron scattering investigations showed that the proton momentum distribution is qualitatively different from that of the bulk water for water confined on a scale of 20 Å. Since the confining potential for the protons is due to the electrons, the electronic ground state of nano-confined water should also be anomalous. X-ray Compton scattering, which probes the ground state of a system, was utilized to understand the ground state configuration of the valence electrons of a particular nano-confined water system, Nafion, a proton exchange membrane (PEM) used in fuel cells. The results showed, for the first time, that the electrons are in a different quantum state from that of bulk water. This difference cannot be explained by empirical models based on weakly interacting molecules. The separation of elements of biological cells is about 20 Å, therefore we would expect the functioning of the cells to be determined by the properties of this nano-confined state.
京都大学 大学院工学研究科 Department of Materials, Science & Engineering, Kyoto University
- Abstract
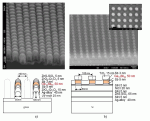
- 「プラズモニック近接場光」を記録再生光源、「ナノドット相変化材料」をメモリ層とする次世代の高速・高密度光記録を目指して、相変化材料Ge10Sb90のナノドットアレイを作製し、そのレーザ誘起結晶化過程を観測した。ビームラインBL40XUのポンププローブ法による時分割X線回折(XRD)と反射率変化測定の結果、直径・高さ50 nmのGe10Sb90アモルファスナノドットは、300ピコ秒の近赤外レーザ照射に誘起されて結晶化し反射率増大を示すことが確認され、また、励起→結晶化の遅延時間は層構成の工夫により15~20 nsまで短縮された。これらの結果は、相変化ナノドットが、高密度・高速次世代光記録に適用可能なポテンシャルを有することを示す。
[1]Department of Chemistry, University of California - Davis, [2]Physical Biosciences Division, Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, [3]Department of Biochemistry, Virginia Polytechnic Institute, [4]Max-Planck-Institut für Chemische Energiekonversion, [5]Department of Chemical Engineering, Stanford University, [6]School of Chemistry, University of East Anglia, [7]Research & Utilization Division, JASRI
2. SACLA通信/SACLA COMMUNICATIONS
(独)理化学研究所 放射光科学総合研究センター XFEL研究開発部門 XFEL Research and Development Division, RIKEN
- Abstract
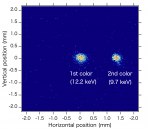
- XFELは波長可変性と横方向のコヒーレンスに加え、フェムト秒の短パルス性、100 GWレベルの高ピークパワーを兼ね備えており、超高速現象や反応過程を動的に精度よく観察するには最適なX線光源である。2色XFELでは、シケインを挟んでアンジュレータを2つのセクションに分割し、各セクションで異なる波長でレーザーを発振させ、2つのX線パルスを生成する。各セクションのK値を調整することで2波長とも可変であり、2パルス間の時間差はシケインで電子ビームを遅延させることにより高精度で調整することができる。同じ電子ビームから2つのパルスを生成するため、2パルス間の時間ジッターはほとんどなく、X線ポンプX線プローブ実験など2色XFELを用いた新しい実験手法の開拓が期待される。
(公財)高輝度光科学研究センター XFEL利用研究推進室 XFEL Utilization Division, JASRI
- Abstract
- X線自由電子レーザーは、大強度のフェムト秒X線レーザーパルスを発生できる新しい高輝度光源である。X線自由電子レーザー施設SACLAでは、供用開始から約2年間、物理、化学、生物、材料科学など様々な分野で利用研究の開拓が進められてきた。本稿では、SACLAにおけるコヒーレント回折イメージング解析とシリアルフェムト秒結晶構造解析の現状を紹介する。併せて、これらのSACLA利用実験のデータ収集および解析の共通基盤システムの現状を紹介する。
3. 研究会等報告/WORKSHOP AND COMMITTEE REPORT
(公財)高輝度光科学研究センター 利用研究促進部門 Research & Utilization Division, JASRI
(公財)高輝度光科学研究センター 制御・情報部門 Controls and Computing Division, JASRI
SPring-8萌芽的研究アワード審査委員会 委員長 Chair of The SPring-8 Budding Researchers Award Committee
4. SPring-8通信/SPring-8 COMMUNICATIONS
5. 談話室・ユーザー便り/USER LOUNGE・LETTERS FROM SPring-8 USERS
SPring-8ユーザー協同体(SPRUC)庶務幹事/(独)理化学研究所 放射光科学総合研究センター RIKEN SPring-8 Center, RIKEN