Volume 25, No.4
Autumn issue 2020
1. 最近の研究から/FROM LATEST RESEARCH
[1]名古屋大学 大学院理学研究科 Graduate School of Science, Nagoya University、[2]富山大学 教養教育院 Institute of Liberal Arts and Sciences, University of Toyama、[3]名古屋大学 物質科学国際研究センター Research Center for Materials Science, Nagoya University
- Abstract
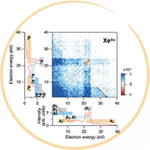
- 極紫外域における超高速非線形原子過程の基礎的理解を目指し、磁気ボトル型光電子分光器を用いた多電子−イオンコインシデンス計測の導入を行った。理研SACLAの軟X線ビームライン(BL1)から得られる極紫外レーザー(91 eV、30 fs、1.6 × 1012 W/cm2)を用いてXe原子の非線形多重イオン化過程を調べたところ、Xe4+イオンと同時計測された電子スペクトルには、Xe 4d内殻二重空孔状態への2光子吸収とこれに引き続くオージェ電子ピークが見出された。Xe4+イオンの生成にはXe2+イオンの4d内殻イオン化を経由する経路が知られていたものの、多電子−イオンコインシデンス計測を用いることによって初めて、4d空孔状態の寿命と競合して生成する4d二重空孔状態がXeの非線形光学応答に大きく寄与していることが明らかとなった。
(国)理化学研究所 放射光科学研究センター XFEL研究開発部門 XFEL Research and Development Division, RIKEN SPring-8 Center
- Abstract
- 超高ピーク輝度、ほぼ完全な空間コヒーレンス、約10 fsの超短パルス幅という、これまでのX線光源にはない特性をもつX線自由電子レーザー(XFEL)の登場により、X線計測技術は飛躍的な進歩を遂げている。本研究では、新たなXFEL計測技術の開拓を目的とし、X線ビームスプリッタやダメージフリーなチャネルカット結晶、ギャップ幅が約100 μmのマイクロチャネルカット結晶といった新奇結晶光学素子を開発し、分割遅延光学系によるピコ秒間隔のダブルパルスXFELや反射型セルフシード法による高強度狭帯域XFELの発生を実現した。両技術を複合的に活用することで、高強度なダブルパルスXFELが発生でき、原子スケールの自発的な揺らぎの緩和時間や、XFEL照射によって生じる電子状態や結晶構造等の変化を、数フェムト秒から最大数百ピコ秒に渡って計測できると期待される。
Institute for Planetary Materials, Okayama University / Bayerisches Geoinstitut, University of Bayreuth
- Abstract
- High-pressure and high-temperature experiments are indispensable to understand the Earth's interior. Large volume press (LVP) can generate pressures in a much larger volume than that of the diamond anvil cell, and has been widely used in various X-ray measurements revealing physical and chemical properties of minerals under the Earth's mantle conditions. Development of X-ray transparent cell in LVP is, thus, essential. In this study, I developed a boron-doped diamond (BDD) heating element, which is both refractory and X-ray transparent; and a boron-MgO composite pressure medium, which is highly X-ray transparent without sacrificing the pressure generation efficiency. With BDD heater, I succeeded in generating temperature as high as 4000 K at ~15 GPa. Then, I tried to apply the BDD heating element to in-situ falling sphere viscometry, which is the best method to directly measure viscosity under high-pressure conditions. Thanks to the ideal characteristics of BDD heater, I succeeded in measuring viscosity of forsterite, enstatite and diopside liquids up to 30 GPa by in-situ falling sphere viscometry. The new viscosity data set infers that a bridgmanite-enriched layer should form at the top lower-mantle during the cooling of magma ocean.
2. 研究会等報告/WORKSHOP AND COMMITTEE REPORT
(公財)高輝度光科学研究センター 放射光利用研究基盤センター 産業利用推進室 Industrial Application Division, Center for Synchrotron Radiation Research, JASRI
[1]SPring-8ユーザー協同体(SPRUC)行事幹事/筑波大学 数理物質系 Faculty of Pure and Applied Sciences, University of Tsukuba、[2]岡山大学 異分野基礎科学研究所 Research Institute for Interdisciplinary Science, Okayama University
3. SPring-8/SACLA通信/SPring-8/SACLA COMMUNICATIONS
(公財)高輝度光科学研究センター 放射光利用研究基盤センター 産業利用推進室 Industrial Application Division, Center for Synchrotron Radiation Research, JASRI
(公財)高輝度光科学研究センター XFEL利用研究推進室 XFEL Utilization Division, JASRI
4. 談話室・ユーザー便り/USER LOUNGE・LETTERS FROM USERS
SPring-8ユーザー協同体(SPRUC)会長/広島大学 大学院先進理工系科学研究科 Graduate School of Advanced Science and Engineering, Hiroshima University
[1]SPring-8利用推進協議会事務局/(公財)高輝度光科学研究センター 常務理事 Executive Managing Director of JASRI、[2](公財)高輝度光科学研究センター 利用推進部 User Administration Division, JASRI