Volume 17, No.3
August issue 2012
1. 最近の研究から/FROM LATEST RESEARCH
[1]Sincrotrone Trieste、[2]京都大学 原子炉実験所 Kyoto University Research Reactor Institute、[3]日本原子力研究開発機構 量子ビーム応用研究部門 Quantum Beam Science Directorate, JAEA
- Abstract
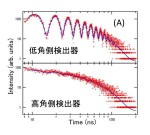
- 核共鳴散乱X線を用いた時間領域干渉計法は、原子・分子サイズの空間相関における1 nsから10 μs程度の緩和を測定可能なユニークな準弾性散乱測定法である。この方法を用いて、層秩序構造を有するスメクティック相状態にある2種の液晶の運動性を調べた。その結果、典型的な液晶とフッ素鎖を導入した両親媒性液晶の分子間相関の緩和時間はその層内と層間でそれぞれほぼ同程度であることが分かり、それにより両親媒性液晶の微視的構造の知見を得ることが出来た。
[1]名古屋市立大学大学院 システム自然科学研究科 Department of Information and Biological Sciences, Nagoya City University、[2]名古屋大学大学院 工学研究科 Department of Applied Physics, Nagoya University、[3]名古屋大学大学院 理学研究科 Department of Chemistry, Nagoya University
- Abstract
- リチウムイオンを1個内包したフラーレンLi+@C60は、正電荷を持った球形の分子であるために、分子それ自体が陽イオンに似た性質を示す。対となる陰イオンにPF6−を用いた場合、Li+@C60とPF6−が交互に配列した岩塩型構造を持つ結晶が得られる。Li+@C60はその結晶中で、高温においてほぼ自由に回転運動している。370 K付近の相転移を境にC60は回転運動を停止し、それより低温で特定の分子配向を持つ。一方、内包されたリチウムイオンは、100 K付近でもC60内部をかなり自由に運動している。100 K以下でリチウムイオンは、C60外部のPF6−との間に働く静電的な引力により、特定の2つの位置に等確率に占有するように温度の低下に伴い徐々に局在していく。
[1](独)国立病院機構西多賀病院 Research Center, NHO Nishitaga National Hospital、[2]東北大学大学院 医学系研究科 Graduate School of Medicine, Tohoku University
- Abstract
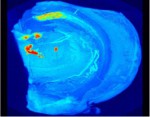
- 通常のX線CTやMRIでは脳内の神経細胞を見ることができない。しかし放射光を光源とする位相差撮像法は吸収CTの1000倍程度の測定感度をもち、脳微細構造の観察が可能である。我々は放射光位相差CTを用いて、脳を切らずに神経細胞を描出する方法を確立した。このことは脳卒中における血管構築と病巣範囲の相互関係、神経難病での病変分布を立体的・系統的に解析出来ることを意味する。本稿では、神経疾患や遺伝子改変動物の解析、再生医療用デバイス開発において放射光CTがいかに強力なツールであるかを紹介する。多くの形態学的情報が得られる放射光CTは、脳機能と脳疾患の研究において重要な位置を占めていくと考えられる。
[1]The Ritchie Centre, Monash Institute for Medical Research, [2]School of Physics, Monash University, [3]Division of Biological Engineering, Monash University, [4]Department of Radiography and Medical Imaging, Monash University, [5]Research & Utilization Division, JASRI
- Abstract
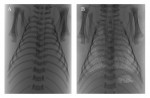
- Lung diseases have a major impact on human health at every stage of life. In newborn infants, respiratory failure is the greatest cause of death and disease, whereas in children, asthma and related airway diseases are a major cause of illness. Similarly, asthma, emphysema and pulmonary fibrosis are major causes of death in adults, but the diagnostic capabilities of current lung imaging modalities are limited by relatively poor spatial and temporal resolutions. Phase contrast (PC) X-ray imaging can image the lung with greatly increased temporal and spatial resolutions, compared with many other modalities. We have applied this technique to investigate factors that promote lung aeration following very premature birth and to measure alterations in lung motion caused by disease. We have demonstrated that lung aeration predominantly results from pressure gradients generated during inspiration, which has overturned almost 40 years of accepted wisdom. Because of this new understanding, we have developed new approaches for facilitating lung aeration in very premature newborns. Specifically we have shown that application of an end-expiratory pressure facilitates lung aeration by preventing liquid from re-entering the airways during expiration. We have also shown that a sustained inflation greatly promotes uniform lung aeration before tidal breathing begins and that expired CO2 levels accurately indicate the degree of lung aeration immediately after birth. By combining PC X-ray imaging with particle image velocimetry, we have also been able to identify how lung diseases affect the speed and direction of lung motion. This technique has the capability of measuring regional lung function with a spatial resolution that is unparalleled by any other current technology.
2. SACLA通信/SACLA COMMUNICATIONS
(公財)高輝度光科学研究センター XFEL研究推進室 XFEL Division, JASRI
- Abstract
- 2012年3月より供用を開始したX線自由電子レーザー施設SACLAの実験ステーションの現状を報告する。SACLAの2012A期の運転では、コヒーレント回折イメージング(CDI)、時間分解X線散乱・回折計測、X線非線形光学、微結晶構造解析などの利用実験が硬X線ビームラインBL3において実施された。また、ビームライン光学系や共用実験装置のための調整実験も行われ、実験ステーションの高度化が進められている。本稿では特にBL3の5個の実験ステーションに注目し、実験ハッチ内の機器構成、ビーム特性、実験制御・データ取得(DAQ)システムなどを紹介する。
3. 研究会等報告/WORKSHOP AND COMMITTEE REPORT
(公財)高輝度光科学研究センター 産業利用推進室 Industrial Application Division, JASRI
4. SPring-8通信/SPring-8 COMMUNICATIONS
5. 談話室・ユーザー便り/USER LOUNGE・LETTERS FROM SPring-8 USERS
SPring-8ユーザー協同体(SPRUC) 会長/東京大学大学院 新領域創成科学研究科 Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, The University of Tokyo