Volume 02, No.1 Pages 17 - 29
3. 共用ビームライン/PUBLIC BEAMLINE
Outline of SPring-8 Public Beamlines under Construction
(from the SPring-8 WWW site*)
日本原子力研究所・理化学研究所 大型放射光施設計画推進共同チーム 利用系グループ JAERI-RIKEN SPring-8 Project Team Experimental Group
Beamline
ーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーー
| ●Public Beamline | |
|---|---|
| ●BL01B1 XAFS | partial operation in Oct. 1997 |
| ●BL02B1 Crystal Structure Analysis | full operation in Oct. 1997 |
| ●BL04B1 High Temperature Research | partial operation in Oct. 1997 |
| ●BL08W High Energy Inelastic Scattering | |
| ●BL09XU Nuclear Resonant Scattering | partial operation in Oct. 1997 |
| ●BL10XU Extremely Dense State | |
| ●BL25SU Soft X-ray Spectroscopy of Solid | |
| ●BL27SU Soft X-ray Photochemistry | |
| ●BL39XU Physicochemical Analysis | partial operation in Oct. 1997 |
| ●BL41XU Bio-Crystallography | partial operation in Oct. 1997 |
| ●Beamline for the Research and Development | |
|---|---|
| ●BL47XU R&D 1 | full operation in Oct. 1997 |
| ●JAERI Beamline |
|---|
| ●RIKEN Beamline |
| ●Location of Beamlines |
|---|
| ●Technical Information of Beamlinem |
|---|
| ●Insertion Device |
________________________________________________
kimura@spring8.or.jp
Last modified : Oct 16,1996
Location of Beamlines (Clickable Map)
ーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーー

BL01B1 — XAFS —
ーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーー
| Location : | BL-01 Bending Magnet #1 BL. |
| Person in Charge : | Tomoya URUGA (e-mail:urugat@spring8.or.jp) |
| Subgroup : | Broad Energy Band XAFS |
| Source Characteristics : | Device | Bending Magnet, Ec=28.9 keV |
| Total power | 220 W (I=100 mA) | |
| Power density | 1.5 kW/mrad2 (I=100 mA) | |
| Source size at 2% coupling | Sx=0.182 mm, Sy=0.058 mm, Sy'=0.065 mrad |
| Optics : | |||
| Distance from source | Optical Element | Function | |
| 32.7 m | first mirror | collimation, higher harmonics elimination | |
| 35.7 m | adjustable inclined double crystal monochromator | monochromatization, sagital focusing | |
| 42.3 m | second mirror | meridional focusing, higher harmonics elimination | |
| X-ray at Sample : | Energy range : 3.5-90 keV Energy resolution : DE/E=10-4 Photon flux : 109-1011 ph/s |
BM1 (02B1) : Crystal Structure Analysis
BM3 (01B1) : XAFS

________________________________________________
@spring8.or.jp
All material on this page and pages on www.spring8.or.jp are copyrighted by SPring-8, 1996.
Last modified: May 1, 1996
BL02B1 — Crystal Structure Analysis —
ーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーー
| Location : | BL-02 Bending Magnet #1 BL. |
| Scientist in Charge : | Yukio NODA (e-mail:ynoda@science.s.chiba-u.ac.jp) |
| In-house Staff : | Hiroyuki KONISHI (e-mail:konishi@sp8sun.spring8.or.jp) |
| Study of structural aspects by fixed energy X-ray beam | |||
| Research Objectives | ・ | Precise structural analysis of new synthesized materials | |
| ・ | Observation of an extremely weak diffraction intensity reflectioing very small structural change. | ||
| Light Source | Bending Magnet | ||
Abstract
The beamline called Crystal Structure Analysis is assigned to four subgroups, that is, Structural Phase transition, Highly Precise Molecular Crystallography, Diffuse Scattering and High-Resolution Powder groups. These groups handle materials to study structural aspects by fixed energy X-ray beam commonly. However, there are divergences in techniques such as crystal size, variation of atmospheres of samples, requirements of resolution function for the diffraction experiments and so on. The structural phase transition group became the group leader of this project to organize and converge the requirement for the system settled on the beamline.
The main concept of this beamline is to construct the machine as the general purpose for the diffraction experiments to include all of necessary demands of these four groups. They proposed the high flux and high energy beamline by using the radiation generated from a bending magnet in order.
- to observe various weak diffraction such as diffuse scattering or superlattice diffraction utilizing the high flux radiation,
- to collect a lot of diffraction data for precise structural analysis by utilizing high energy radiation and expanding the observable reciprocal lattice volume.
The experimental station is designing by the collaboration of four groups. The central part of the station is the sevenaxes diffractometer. It is very similar with the conventional six-axes diffractometer commonly used at many beamlines of synchrotron radiation facilities, and one extra two-theta axis is added. The purpose of the extra axis is to be specialized for the conventional structure analysis to give the high speed motor function. Off-center type chi-cradle is planned to put a cryostat, a furnace, a vacuum chamber and a spindle for powder sample on the phi-circle. Many other optional tools is be planning, for instance, a high precision solar slit, Imaging plate system for photographic method.
________________________________________________
konishi@spring8.or.jp
All material on this page and pages on www.spring8.or.jp are copyrighted by SPring-8, 1996.
Last modified: May 8, 1996
BL04B1 — High Temperature Research —
ーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーー
| Location : | BL-04 Bending Magnet #1 BL. |
| Scientist in Charge : | Kazuhiko TSUJI (e-mail:tsuji@phys.keio.ac.jp) |
| In-house Staff : | Wataru UTSUMI (e-mail:utsumi@spring8.or.jp) |
| Scientific Applications | X-ray diffraction for expanded fluids, liquids, and liquid alloys, XAFS, Small-angle x-ray scattering, Anomalous x-ray scattering (AXS) for multi-componet system. | |
| Light Source | Bending Magnet, 10-150 keV | |
| Beam characteristics at sample | 1. Energy range 10-150 keV 2. Energy resolution 5(eV), white 3. Beam Size 1×1 mm2 4. Beam Divergence vertical < 0.05 mrad, horizontal < 0.5 mrad 5. Photon flux 1010 photons/sec/mm2/0.1%b.w. 6. Beam Stability 0.1(mm) 7. Others white x-ray and moochomatized x-ray | |
Abstract
The experimental hutches for the high temperature research will be built at the BL04B1 bending magnet beamline. This beamline has no monochrometer and white x-rays will be supplied for the experiment. Two scientific subgroups, high pressure mineral physics group and high temperature group, are planning to carry out their experiment in the two experimental stations tandemly built on this beamline.
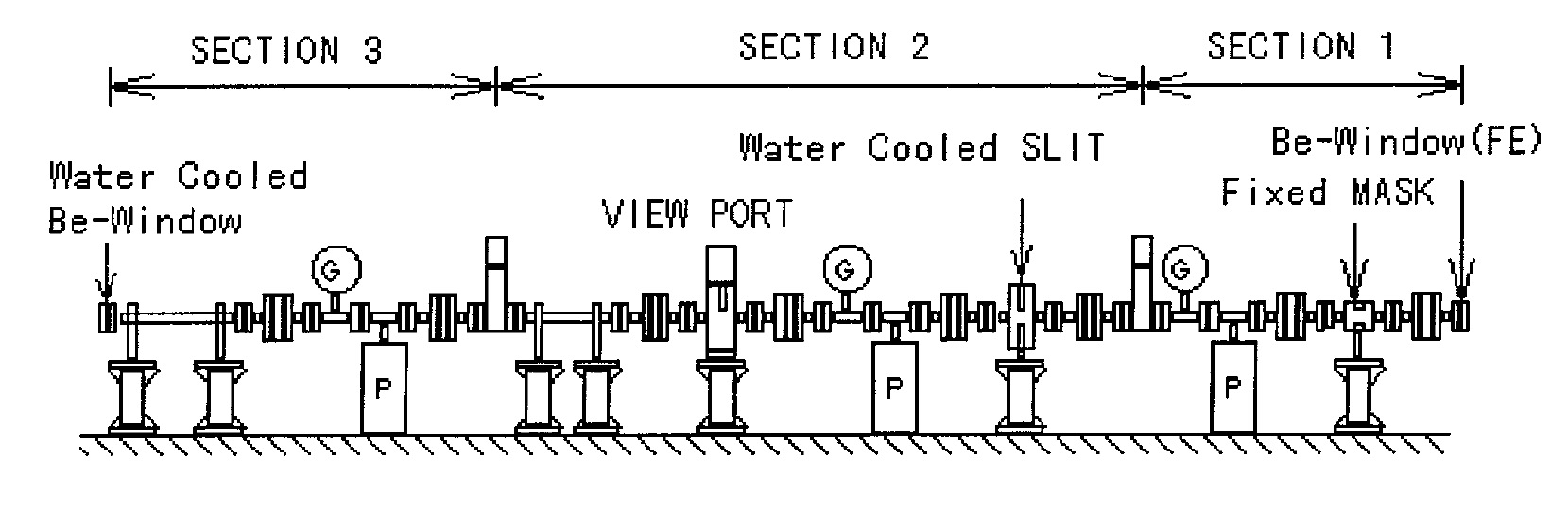
Fig.1 Schematic view of transport channel of BL04B1
High Pressure Mineral Physics
Research Subjects
- Structure of the Earth’s Mantle and Core
- Magma and Molten Metal in the Earth’s Interior
- In situ Observation of Diamond Synthesis
Facilities
- 1500 ton Large Volume Press with 6-8 Multi-Anvil Type High Pressure System 40 GPa, 2500 C
- Vertical and Horizontal Goniometer
The aim of the high pressure mineral physics group is to reveal the origin, evolution and present state of the internal structure of the Earth and other planets. For this purpose, various properties of planetary materials, such as iron, silicates, hydrogen and helium, will be investigated under high pressures and high temperatures. In particular, in situ x-ray diffraction experiment under high pressure and high temperature will be mainly carried out using the polychromatic x-rays from a bending magnet. The extreme pressure and temperature conditions corresponding to those of planetary interiors can be obtained with a multi-anvil type high pressure apparatus, which will be installed on this beamline. This high pressure apparatus has a 1500 ton ram-force uniaxial press with a cubic anvil type guide block, and is operated in the two-stage mode (so called 6-8 system) to reach the desired P-T conditions. This system has a capability of generating pressures up to 40 GPa and a temperature of 3000 K using a solid pressure medium. For the x-ray experiments, two single-axis goniometers (vertical and horizontal directions) are equipped by the high pressure press. The Ge solid state detector is used for the energy dispersive x-ray diffraction experiments.
High Temperature
Research Subjects
- Structural Studies for Expanded Fluid Metals and Semiconductors
- Partial Structures in Multi-Component System
- Anomalous X-ray Scattering
- XAFS
- Structural Studies at Extremely High Temperatures
Facilities
- High Pressure Gas Vessel
Helium 2000 kg/cm2, 1650 C - Horizontal Goniometer
- Protection Wall
The high temperature group is planning to investigate the structural properties of disordered materials under high temperatures. One of the biggest topics is the structural studies of expanded fluid metals and semiconductors. When liquid metals are heated and pressure is applied to prevent boiling, significant density decreases can be achieved. When temperature is elevated at low pressure, a first-order phase transition from liquid to gas occurs accompanied with increasing pressure, and disappears at the critical point. At the pressure higher than this critical pressure, the volume of expanded fluid can be changed continuously in a wide range by heating. The structure of these expanded fluids, such as Hg and Se, will be investigated in a wide density range by the x-ray diffraction measurements and the small-angle x-ray scattering. In the experimental station, a high pressure gas vessel and an energy dispersive x-ray diffractometer will be installed. This high pressure vessel permits x-ray diffraction measurements at high temperature and pressure up to 1650 C and 2000 kg/cm2. Since helium high pressure gas is used as pressure medium, all these facilities will be placed in small rooms surrounded by the protection wall built inside the hutch.
________________________________________________
utsumi@spring8.or.jp
All material on this page and pages on www.spring8.or.jp are copyrighted by SPring-8, 1996.
Last modified: July 30, 1996
BL08W —High Energy Inelastic Scattering —
ーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーー
| Location : | BL-08 Insertion Device BL. |
| Person in Charge : | Hitoshi YAMAOKA (e-mail:yamaoka@spring8.or.jp) |
| Subgroup : | High Energy Inelastic Scattering |
| Scientific Applications : | Magnetic Compton Scattering High-resolution Compton Scattering High-energy Bragg Scattering |
| Source Characteristics : | Device | Elliptic multipole wiggler |
| lu | 12 cm | |
| N | 37 | |
| Critical energy | 42.6 keV at Ky=11.2 | |
| Total Power | 17.9 kW at Ky=11.2 | |
| Peak Power density | 160 kW/mrad2 at Ky=11.2 | |
| On-aixs degree of circular polarization | 0.76 at 300 keV, Ky=11.2, Kx=0.6 |
| Station A : (for Magnetic Compton Scattering) |
Optics : | Asymmetric Johanson monochromator, Si(771) X-ray energy : 300 keV Energy resolution : DE/E = 5x10-3 X-ray beam size at sample : 3 mm(H)x1 mm(W) X-ray flux at sample : 5x1012 ph/s at 300 keV |
| Station B : (for High-resolution Compton Scattering) |
Optics : | Doubly bent monochromator, Si(400) X-ray energy : 100-150 keV Energy resolution : DE/E<1x10-3 X-ray beam size at sample : 0.5 mm(H)x0.5 mm(W) X-ray flux at sample : 3.3x1013 ph/s at 100 keV |
________________________________________________
@spring8.or.jp
All material on this page and pages on www.spring8.or.jp are copyrighted by SPring-8, 1996.
Last modified: May 1, 1996
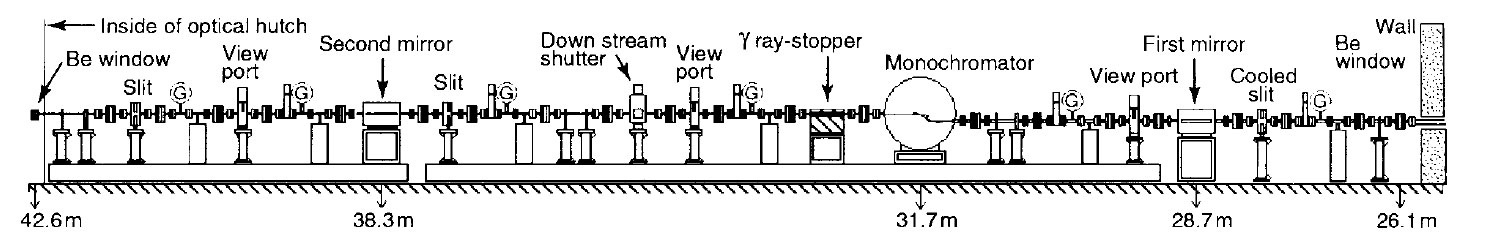
BL09XU — Nuclear Resonant Scattering —
ーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーー
| Location : | BL-09 Insertion Device BL. |
| Person in Charge : | Taikan HARAMI (e-mail:taikan@spring8.or.jp) |
| Subgroup : | Nuclear Resonant Scattering Surface and Interface Structure |
| Source Characteristics : | Device | In-vacuum-type undulator |
| lu | 3.2 cm | |
| N | 140 | |
| Tunable range | 6-80 keV | |
| Brilliance | 1.5x1019 ph/s/mrad2/mm2/0.1%b.w. at 14.4 keV | |
| Total Power | 1.31 kW at 14.4 keV | |
| Power density | 141 kW/mrad2 at 14.4 keV | |
| Source size | Sx=0.41 mm, Sy=0.035 mm, Sx'=0.017 mrad, Sy'=0.0039 mrad |
| Optics : | Distance from source | Optical Element | Description |
| 40 m | Rotated-inclined double crystal monochromator | Energy resolution : DE/E~10-4 |
XU2 (09XU) : Nuclear Resonant Scattering
________________________________________________
taikan@spring8.or.jp
All material on this page and pages on www.spring8.or.jp are copyrighted by SPring-8, 1996.
Last modified: July 2, 1996
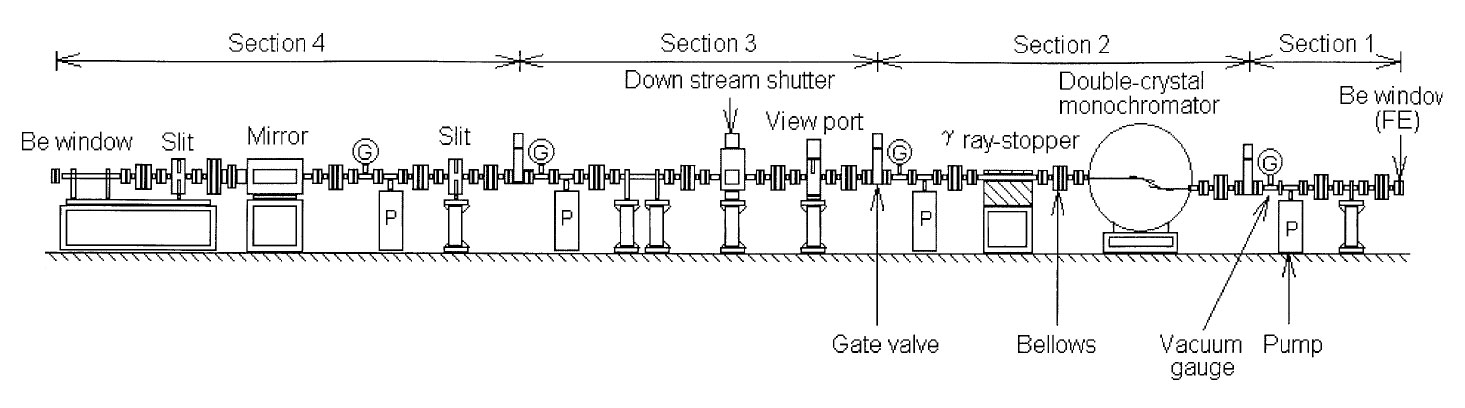
BL10XU — Extremely Dense State —
ーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーー
| Location : | BL-10 Insertion Device BL. |
| Person in Charge : | Kentaro SUZUYA (e-mail:suzuya@sp8sun.spring8.or.jp) |
| Subgroup : | Structural Properties of Extremely Dense Materials High Brilliance XAFS |
| Source Characteristics : | Device | In-vacuum-type undulator |
| lu | 3.2 cm | |
| N | 140 | |
| Tunable range | >5 keV | |
| Brilliance | 2x1019 ph/s/mrad2/mm2/0.1%b.w.(I=100 mA) | |
| Total Power | 5 kW | |
| Power density | 300 kW/mrad2 |
| Optics : | ||
| Distance from source | Optical Element | Function |
| 36 m | rotated-inclined double crystal monochromator | monochromatization of 5-60 keV X-rays |
| 43 m | double-flat mirror system (fixed exit double mirrors) | cut off energy : 10-20 keV |
| 56 m | Bragg Fresnel Lens | |
XU3 (10XU) : Extremely Dense State

________________________________________________
suzuya@spring8.or.jp
All material on this page and pages on www.spring8.or.jp are copyrighted by SPring-8, 1996.
Last modified: July 3, 1996
BL25SU — Soft X-ray Spectroscopy of Solid —
ーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーー
| Location : | BL-25 Insertion Device BL. |
| Person in Charge : | Y. SAITOH (e-mail:ysaitoh@spring8.or.jp) |
| Subgroup : | Soft X-ray Spectroscopy of Solid |
| Source Characteristics : | Device | Twin helical undulator Fast helicity modulation |
| lu | 120 mm | |
| N | 12 | |
| Tunable range | 0.5-3 keV | |
| Brilliance | 6.65x1017 ph/s/mrad2/mm2/0.1%b.w. | |
| Total Power at 1 keV | 667.5 W | |
| Power density at 1 keV | 0.862 kW/mrad2 | |
| Source size | Sx=0.41 mm, Sy=0.035 mm, Sx'=0.033 mrad, Sy'=0.029 mrad |
| Optics : | ||
| Distance from source | Optical Element | Function |
| 38 m | cylindrical mirror (Mh) | deflection and horizontal focusing |
| 40 m | spherical mirror (Mv) | vertical focusing at the entrance slit |
| 50-71.9 m | constant deviation monochromator with varied-space plane gratings (S1-M1 or M2-G-S2) |
monochromatization |
| 76.4 m, 80.9 m | cylindrical mirrors (M3, M4) | focusing the beam onto the sample |
| X-ray at Sample : | Energy resolution : E/DE > 10000 Photon flux : > 1013 ph/s Beam size : < 0.1 mm |
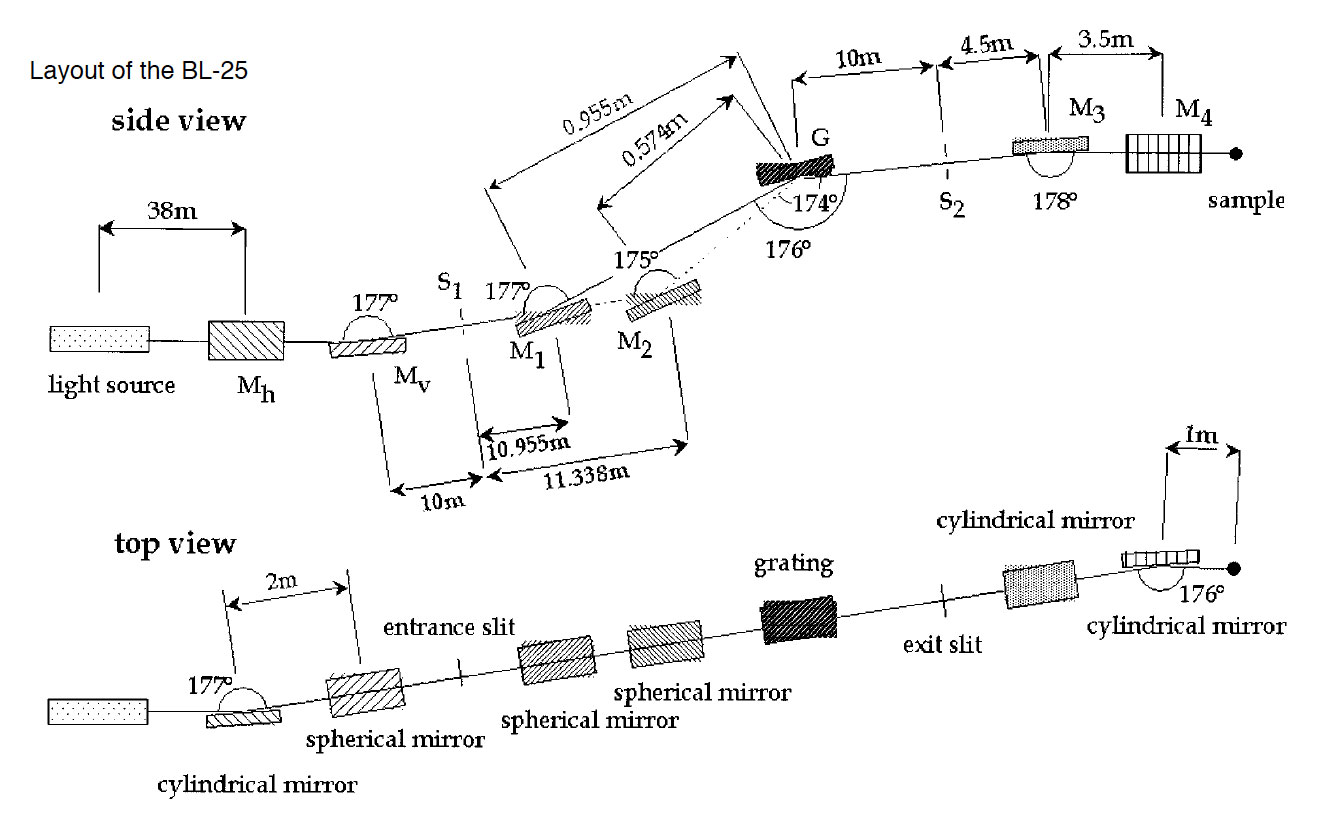
________________________________________________
ysaitoh@sp8sun.spring8.or.jp
All material on this page and pages on www.spring8.or.jp are copyrighted by SPring-8, 1996.
Last modified: May 1, 1996
BL27SU —Soft X-ray Photochemistry—
ーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーー
| Location : | BL-27 Insertion Device BL. |
| Person in Charge : | T. Sekiguchi (e-mail:tsekiguc@spring8.or.jp) |
| Subgroup : | Soft X-ray Photochemistry Soft X-ray CVD |
| Scientific Applications : | High resolution molecular spectroscopy Photoionization dynamics by various correlation measurements Dynamics of inner-shell excited molecules Production and dynamics of novel core-excited states by SR(UR)-laser double resonance techniques Site-specific dissociation processes of adsorbed molecules Growth of thin film of functional material Micro fabrication by functional material etching Clarification of the reaction mechanics for deposition and process |
| Source Characteristics : | Device | Figure-8 undulator |
| lu | 100 mm | |
| N | 44 | |
| Tunable range | 0.5-5 keV | |
| Brilliance | 1.1x1018 ph/s/mrad2/mm2/0.1%b.w. at 500 eV (I=100 mA) | |
| Total Power | 2.7 kW at 1st harmonic(500 eV) | |
| Power density | 1.7 kW/mrad2 at 1st harmonic(500 eV) |
| X-ray at Sample : | Energy range : 0.5-2 keV Linearly polarized Photon flux : 1012 ph/s Beam size : 0.5x0.5 mm2 Resolution : E/DE=10000 and microbeam capability of several-some tens micrometers diameter in the energy range of 0.5-5 keV |

MO’, MO : Horizontally deflecting mirror, M1 : Vertically focusing mirror
Monochromator/ S1 : Entrance slit, S2 : Exit slit, M2 : Focusing mirror, G : Grating
M3 : refocusing mirror, Q : Sample position
________________________________________________
tsekiguc@spring8.or.jp
Last modified: Aug. 6, 1996
BL39XU — Physicochemical Analysis —
ーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーー
| Location : | BL-39 Insertion Device BL. |
| Person in Charge : | Shunji GOTO (e-mail:sgoto@spring8.or.jp) |
| Subgroup : | X-ray Magnetic Absorption and Scattering Spectrochemical Analysis Medical Application |
| Source Characteristics : | Device | In-vacuum-type undulator |
| Period length | 3.2 cm | |
| Peroid number | 140 | |
| Tunable range | 5-70 keV(fundamental-5th) | |
| Brilliance | 2x1019 ph/s/mrad2/mm2/0.1%b.w.(I=100 mA) | |
| Total Power | 11 kW at 5 keV, K=2.3 | |
| Power density | 470 kW/mrad2 |
| Optics : | ||
| Distance from source | Optical Element | Function |
| 36 m | rotated-inclined double crystal monochromator | monochromatization, high heat load elimination |
| 44 m | platinum coated plane mirror | higher harmonics elimination, horizontal deflection |
| X-ray at Sample : | Energy range : 5-20 keV Energy resolution : 2x10-4 Photon flux : 1015 ph/s Beam divergence : < 0.1 mrad Beam size : < 1 mm |
Beamline layout

________________________________________________
sgoto@spring8.or.jp
All material on this page and pages on www.spring8.or.jp are copyrighted by SPring-8, 1996.
Last modified: May 1, 1996
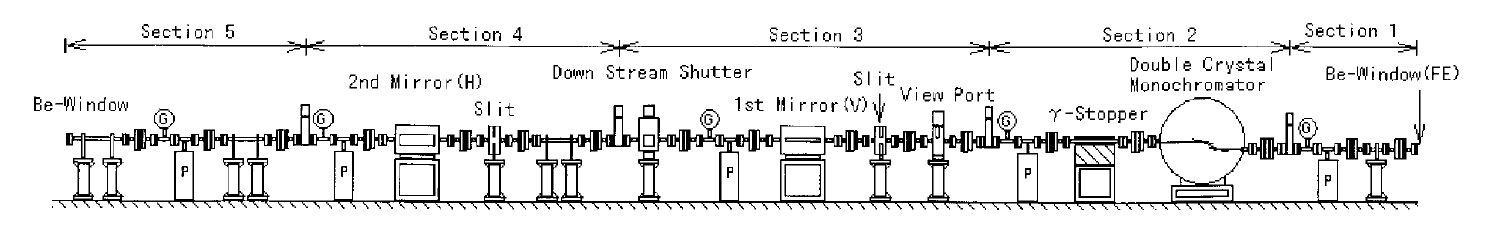
BL41XU — Bio-Crystallography —
ーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーー
| Location : | BL41- Insertion Device BL. |
| Person in Charge : | Nobuo KAMIYA (e-mail:nkamiya@postman.riken.go.jp) |
| Subgroup : | Biological Structure X-ray Structural Biology |
| Source Characteristics : | Device | In-vacuum-type undulator |
| Period length | 3.2 cm | |
| Peroid number | 140 | |
| Tunable range | > 9 keV | |
| Brilliance | 2x1019 ph/s/mrad2/mm2/0.1%b.w.(I=100 mA) | |
| Total Power | 5 kW | |
| Power density | 300 kW/mrad2 |
| Optics : | ||
| Distance from source | Optical Element | Function |
| 35.9 m | rotated-inclined double crystal monochromator | elimination of heat load, monochromatization |
| 39.5 m | vertical focusing mirror | 3:1 demagnification |
| 44.0 m | horizontal focusing mirror | 5:1 demagnification |
| X-ray at Sample : | Energy range : 9-38 keV Energy resolution : 2x10-4(< 10-3 over 20 keV) Photon flux : 1014 ph/s Beam divergence : 0.1 mrad Beam size : 0.1 mm |
________________________________________________
nkamiya@postman.riken.go.jp
Last modified: Aug.7, 1996








